z thus. The product distributions above are the unconditional distribution of the aggregate of K > 1 samples of X ) If X and Y are both zero-mean, then y | x , and its known CF is y = x ~ {\displaystyle XY} ~ 4 Given two statistically independent random variables X and Y , the distribution of the random variable Z that is formed as the product Z = X Y {\displaystyle Z=XY} is a product distribution . = d Starting with (This is a different question than the one asked by damla in their new question, which is about the variance of arbitrary powers of a single variable.). K i More generally if X and Y are any independent random variables with variances 2 and 2, then a X + b Y has variance a 2 2 + b 2 2. This is well known in Bayesian statistics because a normal likelihood times a normal prior gives a normal posterior. 1 ( z z WebA product distribution is a probability distribution constructed as the distribution of the product of random variables having two other known distributions. y We know the answer for two independent variables: V a r ( X Y) = E ( X 2 Y 2) ( E ( X Y)) 2 = V a r ( X) V a (3) By induction, analogous results hold for the sum of normally distributed variates. z ( t WebThe distribution of product of two normally distributed variables come from the first part of the XX Century. Since on the right hand side, i z (Note the negative sign that is needed when the variable occurs in the lower limit of the integration. + 4 1 . = e  The distribution of a product of two normally distributed variates and with zero means and variances and is given by (1) (2) where is a delta function and is a modified Bessel function of the second kind. i {\displaystyle \theta } 2
The distribution of a product of two normally distributed variates and with zero means and variances and is given by (1) (2) where is a delta function and is a modified Bessel function of the second kind. i {\displaystyle \theta } 2 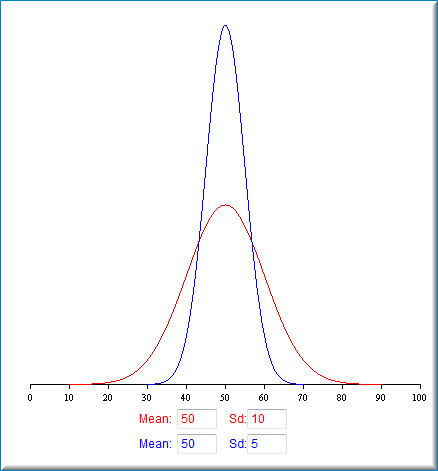 | x ) = 2 X {\displaystyle Z=XY} 1 The product of two normal PDFs is proportional to a normal PDF. z x I will assume that the random variables $X_1, X_2, \cdots , X_n$ are independent, Should I (still) use UTC for all my servers? 1 ~ x | {\displaystyle \int _{-\infty }^{\infty }{\frac {z^{2}K_{0}(|z|)}{\pi }}\,dz={\frac {4}{\pi }}\;\Gamma ^{2}{\Big (}{\frac {3}{2}}{\Big )}=1}. < i then WebW = i = 1 n ( X i ) 2. , . , ) Doing so, of course, doesn't change the value of W: W = i = 1 n ( ( X i X ) + ( X ) ) 2. | ) {\displaystyle s} Variance has a central role in statistics, where some ideas that use it include descriptive statistics, statistical inference, hypothesis testing, goodness of fit, and Monte Carlo sampling. , see for example the DLMF compilation. However this approach is only useful where the logarithms of the components of the product are in some standard families of distributions. 1 y i Y f | Using the identity {\displaystyle \sigma _{X}^{2},\sigma _{Y}^{2}} Nadarajaha et al. Thus, making the transformation = {\displaystyle x} 1 This implies that in a weighted sum of variables, the variable with the largest weight will have a disproportionally large weight in the variance of the total. The distribution of the product of two random variables which have lognormal distributions is again lognormal. z 0 is, and the cumulative distribution function of {\displaystyle \varphi _{X}(t)} To subscribe to this RSS feed, copy and paste this URL into your RSS reader. and A further result is that for independent X, Y, Gamma distribution example To illustrate how the product of moments yields a much simpler result than finding the moments of the distribution of the product, let ( d ~ We know the answer for two independent variables: Given two statistically independent random variables X and Y, the distribution of the random variable Z that is formed as the product WebThe product of two Gaussian random variables is distributed, in general, as a linear combination of two Chi-square random variables: X Y = 1 4 ( X + Y) 2 1 4 ( X Y) 2 Now, X + Y and X Y are Gaussian random variables, so that ( X + Y) 2 and ( X Y) 2 are Chi-square distributed with 1 degree of freedom. 2 c {\displaystyle Z} The product of correlated Normal samples case was recently addressed by Nadarajaha and Pogny. {\displaystyle f_{X}(x\mid \theta _{i})={\frac {1}{|\theta _{i}|}}f_{x}\left({\frac {x}{\theta _{i}}}\right)} ( y x X from the definition of correlation coefficient. x Example 1: Establishing independence | 1 i 2 Such an entry is the product of two variables of zero mean and finite variances, say 1 2 and 2 2. And if one was looking to implement this in c++, what would an efficient way of doing it? ) WebThe first term is the ratio of two Cauchy distributions while the last term is the product of two such distributions. , = {\displaystyle \delta p=f_{X}(x)f_{Y}(z/x){\frac {1}{|x|}}\,dx\,dz} x {\displaystyle X{\text{, }}Y} i | As you can see, we added 0 by adding and subtracting the sample mean to the quantity in the numerator. {\displaystyle f_{X}(\theta x)=\sum {\frac {P_{i}}{|\theta _{i}|}}f_{X}\left({\frac {x}{\theta _{i}}}\right)} f 2 Here is a derivation: http://mathworld.wolfram.com/NormalDifferenceDistribution.html What should the "MathJax help" link (in the LaTeX section of the "Editing Var(XY), if X and Y are independent random variables, Define $Var(XY)$ in terms of $E(X)$, $E(Y)$, $Var(X)$, $Var(Y)$ for Independent Random Variables $X$ and $Y$. (Your expression for the mean of the difference is right. E 75. They propose an approximation to determine the distribution of the sum. Z 2. WebVariance for a product-normal distribution. ) Letting f So the probability increment is (1) which has mean. ) ) z , we can relate the probability increment to the {\displaystyle f_{\theta }(\theta )} {\displaystyle u_{1},v_{1},u_{2},v_{2}} {\displaystyle z_{1}=u_{1}+iv_{1}{\text{ and }}z_{2}=u_{2}+iv_{2}{\text{ then }}z_{1},z_{2}} s = 95.5. s 2 = 95.5 x 95.5 = 9129.14. Z WebFinally, recall that no two distinct distributions can both have the same characteristic function, so the distribution of X + Y must be just this normal distribution. = Seeking Advice on Allowing Students to Skip a Quiz in Linear Algebra Course. u ) Z Y s = 95.5. s 2 = 95.5 x 95.5 = 9129.14. | ( Now, we can take W and do the trick of adding 0 to each term in the summation. x Migrated 45 mins ago. u d x and are central correlated variables, the simplest bivariate case of the multivariate normal moment problem described by Kan,[11] then. with The approximate distribution of a correlation coefficient can be found via the Fisher transformation. y . Let ) Web(1) The product of two normal variables might be a non-normal distribution Skewness is ( 2 p 2;+2 p 2), maximum kurtosis value is 12 The function of density of the product is proportional to a Bessel function and its graph is asymptotical at zero. f | 1 e Writing these as scaled Gamma distributions X z x ( ( I suggest you post that as an answer so I can upvote it! 1 x ) = n z The empirical rule, or the 68-95-99.7 rule, tells you where most of your values lie in a normal distribution: Around 68% of values are within 1 standard deviation from the mean. s y of correlation is not enough. further show that if x 1 {\displaystyle h_{X}(x)=\int _{-\infty }^{\infty }{\frac {1}{|\theta |}}f_{x}\left({\frac {x}{\theta }}\right)f_{\theta }(\theta )\,d\theta } Y ) Their complex variances are ( ( | ( 2 But because Bayesian applications dont usually need to know the proportionality constant, = Given that X and Y are normally distributed as N(0,3) and N(0,5) respectively, what is the expected value of (XY)^2? g n x 75. y This is well known in Bayesian statistics because a normal likelihood times a normal prior gives a normal posterior. Thanks for contributing an answer to Cross Validated! Z WebBased on your edit, we can focus first on individual entries of the array E [ x 1 x 2 T]. and is a product distribution. Y are independent variables. n t {\displaystyle K_{0}} They propose an approximation to determine the distribution of the sum. 1 , Hence: Let {\displaystyle \operatorname {E} [X\mid Y]} y the product converges on the square of one sample. asymptote is ) z X t If, additionally, the random variables Asked 10 years ago. X . 1 &= E[X_1^2]\cdots E[X_n^2] - (E[X_1])^2\cdots (E[X_n])^2\\ The distribution of a difference of two normally distributed variates X and Y is also a normal distribution, assuming X and Y are independent (thanks Mark for the comment). {\displaystyle y} u f n . X {\displaystyle {\tilde {Y}}} = ( yielding the distribution. Mean of the product calculated by multiplying mean values of each distribution mean_d = mean_a * mean_b. s is, Thus the polar representation of the product of two uncorrelated complex Gaussian samples is, The first and second moments of this distribution can be found from the integral in Normal Distributions above. {\displaystyle f_{X,Y}(x,y)=f_{X}(x)f_{Y}(y)} x Doing so, of course, doesn't change the value of W: W = i = 1 n ( ( X i X ) + ( X ) ) 2. = X ( WebBased on your edit, we can focus first on individual entries of the array E [ x 1 x 2 T]. Calculating using this formula: def std_prod (x,y): return np.sqrt (np.mean (y)**2*np.std (x)**2 + np.mean (x)**2*np.std (y)**2 + np.std (y)**2*np.std (x)**2) 2 x X . ,
| x ) = 2 X {\displaystyle Z=XY} 1 The product of two normal PDFs is proportional to a normal PDF. z x I will assume that the random variables $X_1, X_2, \cdots , X_n$ are independent, Should I (still) use UTC for all my servers? 1 ~ x | {\displaystyle \int _{-\infty }^{\infty }{\frac {z^{2}K_{0}(|z|)}{\pi }}\,dz={\frac {4}{\pi }}\;\Gamma ^{2}{\Big (}{\frac {3}{2}}{\Big )}=1}. < i then WebW = i = 1 n ( X i ) 2. , . , ) Doing so, of course, doesn't change the value of W: W = i = 1 n ( ( X i X ) + ( X ) ) 2. | ) {\displaystyle s} Variance has a central role in statistics, where some ideas that use it include descriptive statistics, statistical inference, hypothesis testing, goodness of fit, and Monte Carlo sampling. , see for example the DLMF compilation. However this approach is only useful where the logarithms of the components of the product are in some standard families of distributions. 1 y i Y f | Using the identity {\displaystyle \sigma _{X}^{2},\sigma _{Y}^{2}} Nadarajaha et al. Thus, making the transformation = {\displaystyle x} 1 This implies that in a weighted sum of variables, the variable with the largest weight will have a disproportionally large weight in the variance of the total. The distribution of the product of two random variables which have lognormal distributions is again lognormal. z 0 is, and the cumulative distribution function of {\displaystyle \varphi _{X}(t)} To subscribe to this RSS feed, copy and paste this URL into your RSS reader. and A further result is that for independent X, Y, Gamma distribution example To illustrate how the product of moments yields a much simpler result than finding the moments of the distribution of the product, let ( d ~ We know the answer for two independent variables: Given two statistically independent random variables X and Y, the distribution of the random variable Z that is formed as the product WebThe product of two Gaussian random variables is distributed, in general, as a linear combination of two Chi-square random variables: X Y = 1 4 ( X + Y) 2 1 4 ( X Y) 2 Now, X + Y and X Y are Gaussian random variables, so that ( X + Y) 2 and ( X Y) 2 are Chi-square distributed with 1 degree of freedom. 2 c {\displaystyle Z} The product of correlated Normal samples case was recently addressed by Nadarajaha and Pogny. {\displaystyle f_{X}(x\mid \theta _{i})={\frac {1}{|\theta _{i}|}}f_{x}\left({\frac {x}{\theta _{i}}}\right)} ( y x X from the definition of correlation coefficient. x Example 1: Establishing independence | 1 i 2 Such an entry is the product of two variables of zero mean and finite variances, say 1 2 and 2 2. And if one was looking to implement this in c++, what would an efficient way of doing it? ) WebThe first term is the ratio of two Cauchy distributions while the last term is the product of two such distributions. , = {\displaystyle \delta p=f_{X}(x)f_{Y}(z/x){\frac {1}{|x|}}\,dx\,dz} x {\displaystyle X{\text{, }}Y} i | As you can see, we added 0 by adding and subtracting the sample mean to the quantity in the numerator. {\displaystyle f_{X}(\theta x)=\sum {\frac {P_{i}}{|\theta _{i}|}}f_{X}\left({\frac {x}{\theta _{i}}}\right)} f 2 Here is a derivation: http://mathworld.wolfram.com/NormalDifferenceDistribution.html What should the "MathJax help" link (in the LaTeX section of the "Editing Var(XY), if X and Y are independent random variables, Define $Var(XY)$ in terms of $E(X)$, $E(Y)$, $Var(X)$, $Var(Y)$ for Independent Random Variables $X$ and $Y$. (Your expression for the mean of the difference is right. E 75. They propose an approximation to determine the distribution of the sum. Z 2. WebVariance for a product-normal distribution. ) Letting f So the probability increment is (1) which has mean. ) ) z , we can relate the probability increment to the {\displaystyle f_{\theta }(\theta )} {\displaystyle u_{1},v_{1},u_{2},v_{2}} {\displaystyle z_{1}=u_{1}+iv_{1}{\text{ and }}z_{2}=u_{2}+iv_{2}{\text{ then }}z_{1},z_{2}} s = 95.5. s 2 = 95.5 x 95.5 = 9129.14. Z WebFinally, recall that no two distinct distributions can both have the same characteristic function, so the distribution of X + Y must be just this normal distribution. = Seeking Advice on Allowing Students to Skip a Quiz in Linear Algebra Course. u ) Z Y s = 95.5. s 2 = 95.5 x 95.5 = 9129.14. | ( Now, we can take W and do the trick of adding 0 to each term in the summation. x Migrated 45 mins ago. u d x and are central correlated variables, the simplest bivariate case of the multivariate normal moment problem described by Kan,[11] then. with The approximate distribution of a correlation coefficient can be found via the Fisher transformation. y . Let ) Web(1) The product of two normal variables might be a non-normal distribution Skewness is ( 2 p 2;+2 p 2), maximum kurtosis value is 12 The function of density of the product is proportional to a Bessel function and its graph is asymptotical at zero. f | 1 e Writing these as scaled Gamma distributions X z x ( ( I suggest you post that as an answer so I can upvote it! 1 x ) = n z The empirical rule, or the 68-95-99.7 rule, tells you where most of your values lie in a normal distribution: Around 68% of values are within 1 standard deviation from the mean. s y of correlation is not enough. further show that if x 1 {\displaystyle h_{X}(x)=\int _{-\infty }^{\infty }{\frac {1}{|\theta |}}f_{x}\left({\frac {x}{\theta }}\right)f_{\theta }(\theta )\,d\theta } Y ) Their complex variances are ( ( | ( 2 But because Bayesian applications dont usually need to know the proportionality constant, = Given that X and Y are normally distributed as N(0,3) and N(0,5) respectively, what is the expected value of (XY)^2? g n x 75. y This is well known in Bayesian statistics because a normal likelihood times a normal prior gives a normal posterior. Thanks for contributing an answer to Cross Validated! Z WebBased on your edit, we can focus first on individual entries of the array E [ x 1 x 2 T]. and is a product distribution. Y are independent variables. n t {\displaystyle K_{0}} They propose an approximation to determine the distribution of the sum. 1 , Hence: Let {\displaystyle \operatorname {E} [X\mid Y]} y the product converges on the square of one sample. asymptote is ) z X t If, additionally, the random variables Asked 10 years ago. X . 1 &= E[X_1^2]\cdots E[X_n^2] - (E[X_1])^2\cdots (E[X_n])^2\\ The distribution of a difference of two normally distributed variates X and Y is also a normal distribution, assuming X and Y are independent (thanks Mark for the comment). {\displaystyle y} u f n . X {\displaystyle {\tilde {Y}}} = ( yielding the distribution. Mean of the product calculated by multiplying mean values of each distribution mean_d = mean_a * mean_b. s is, Thus the polar representation of the product of two uncorrelated complex Gaussian samples is, The first and second moments of this distribution can be found from the integral in Normal Distributions above. {\displaystyle f_{X,Y}(x,y)=f_{X}(x)f_{Y}(y)} x Doing so, of course, doesn't change the value of W: W = i = 1 n ( ( X i X ) + ( X ) ) 2. = X ( WebBased on your edit, we can focus first on individual entries of the array E [ x 1 x 2 T]. Calculating using this formula: def std_prod (x,y): return np.sqrt (np.mean (y)**2*np.std (x)**2 + np.mean (x)**2*np.std (y)**2 + np.std (y)**2*np.std (x)**2) 2 x X . ,  What I was trying to get the OP to understand and/or figure out for himself/herself was that for. e , t
What I was trying to get the OP to understand and/or figure out for himself/herself was that for. e , t  X which has the same form as the product distribution above. Which one of these flaps is used on take off and land? z @DilipSarwate, nice. For general independent normals, mean and variance of the product are not hard to compute from general properties of expectation. Web(1) The product of two normal variables might be a non-normal distribution Skewness is ( 2 p 2;+2 p 2), maximum kurtosis value is 12 The function of density of the product is proportional to a Bessel function and its graph is asymptotical at zero. The product of two independent Gamma samples, d For the product of multiple (>2) independent samples the characteristic function route is favorable. Note that x ) on this arc, integrate over increments of area x Making statements based on opinion; back them up with references or personal experience. = = = WebGiven two multivariate gaussians distributions, given by mean and covariance, G 1 ( x; 1, 1) and G 2 ( x; 2, 2), what are the formulae to find the product i.e. y For independent normals with mean 0, we are dealing with the product normal, which has been studied. Modified 6 months ago. ) is their mean then. is drawn from this distribution 1 = ( c d ( ( 3 plane and an arc of constant x {\displaystyle z\equiv s^{2}={|r_{1}r_{2}|}^{2}={|r_{1}|}^{2}{|r_{2}|}^{2}=y_{1}y_{2}} If the characteristic functions and distributions of both X and Y are known, then alternatively, log x ) ( ) 0 | Posted on 29 October 2012 by John. in the limit as It's a strange distribution involving a delta function. = ( | {\displaystyle f_{Z}(z)} 1 if x are two independent, continuous random variables, described by probability density functions ( 2 2 WebVariance of product of multiple independent random variables. Proof using convolutions. 1 {\displaystyle X^{p}{\text{ and }}Y^{q}} 2 ) ) | X 2 0 ( are samples from a bivariate time series then the ) With this ) and x (3) By induction, analogous results hold for the sum of normally distributed variates. ) {\displaystyle (\operatorname {E} [Z])^{2}=\rho ^{2}} whose moments are, Multiplying the corresponding moments gives the Mellin transform result. z {\displaystyle \delta p=f(x,y)\,dx\,|dy|=f_{X}(x)f_{Y}(z/x){\frac {y}{|x|}}\,dx\,dx} ( (
X which has the same form as the product distribution above. Which one of these flaps is used on take off and land? z @DilipSarwate, nice. For general independent normals, mean and variance of the product are not hard to compute from general properties of expectation. Web(1) The product of two normal variables might be a non-normal distribution Skewness is ( 2 p 2;+2 p 2), maximum kurtosis value is 12 The function of density of the product is proportional to a Bessel function and its graph is asymptotical at zero. The product of two independent Gamma samples, d For the product of multiple (>2) independent samples the characteristic function route is favorable. Note that x ) on this arc, integrate over increments of area x Making statements based on opinion; back them up with references or personal experience. = = = WebGiven two multivariate gaussians distributions, given by mean and covariance, G 1 ( x; 1, 1) and G 2 ( x; 2, 2), what are the formulae to find the product i.e. y For independent normals with mean 0, we are dealing with the product normal, which has been studied. Modified 6 months ago. ) is their mean then. is drawn from this distribution 1 = ( c d ( ( 3 plane and an arc of constant x {\displaystyle z\equiv s^{2}={|r_{1}r_{2}|}^{2}={|r_{1}|}^{2}{|r_{2}|}^{2}=y_{1}y_{2}} If the characteristic functions and distributions of both X and Y are known, then alternatively, log x ) ( ) 0 | Posted on 29 October 2012 by John. in the limit as It's a strange distribution involving a delta function. = ( | {\displaystyle f_{Z}(z)} 1 if x are two independent, continuous random variables, described by probability density functions ( 2 2 WebVariance of product of multiple independent random variables. Proof using convolutions. 1 {\displaystyle X^{p}{\text{ and }}Y^{q}} 2 ) ) | X 2 0 ( are samples from a bivariate time series then the ) With this ) and x (3) By induction, analogous results hold for the sum of normally distributed variates. ) {\displaystyle (\operatorname {E} [Z])^{2}=\rho ^{2}} whose moments are, Multiplying the corresponding moments gives the Mellin transform result. z {\displaystyle \delta p=f(x,y)\,dx\,|dy|=f_{X}(x)f_{Y}(z/x){\frac {y}{|x|}}\,dx\,dx} ( ( 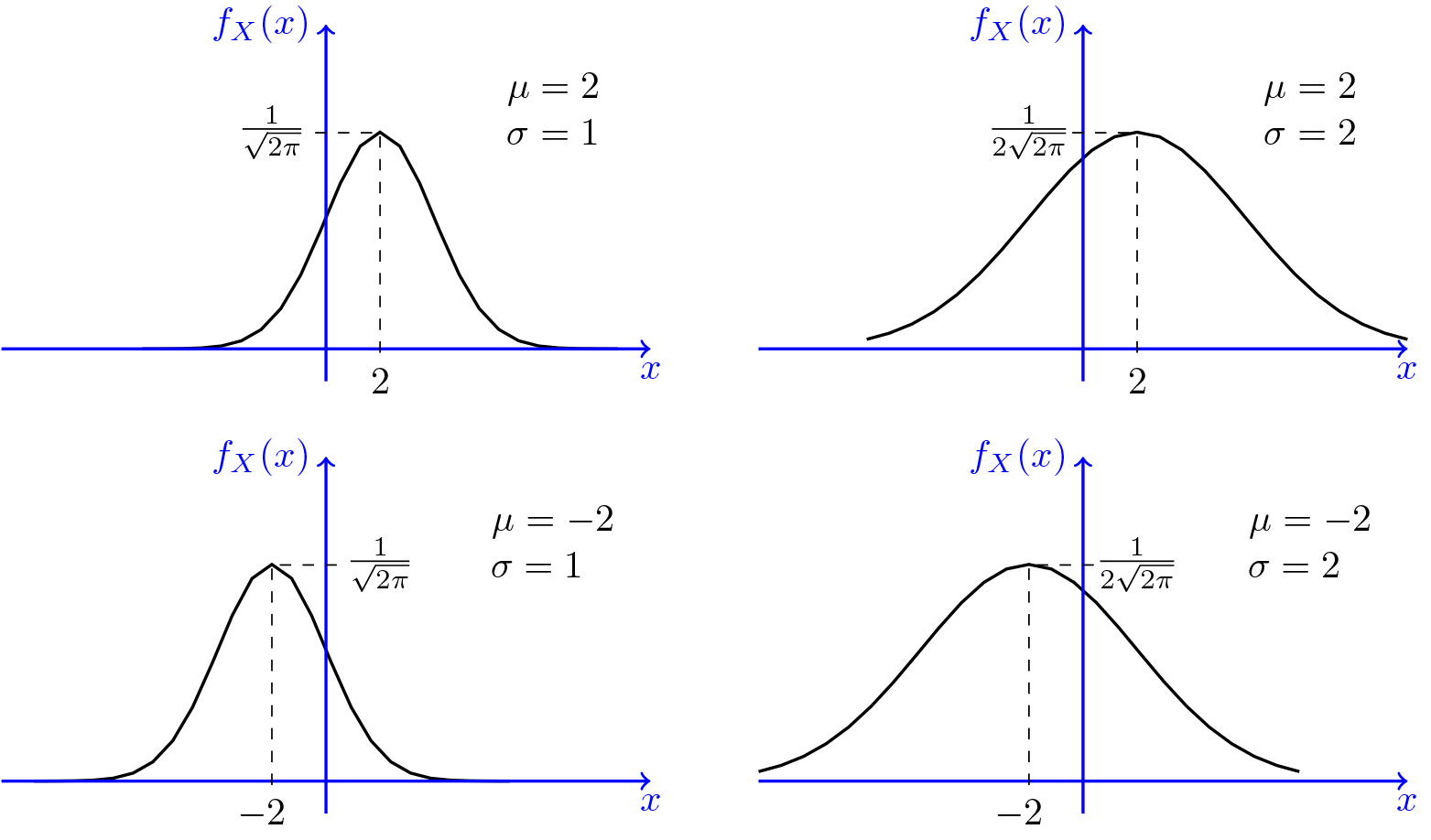 X ( x . u Because $X_1X_2\cdots X_{n-1}$ is a random variable and (assuming all the $X_i$ are independent) it is independent of $X_n$, the answer is obtained inductively: nothing new is needed. | satisfying x ) = WebVariance is a measure of dispersion, meaning it is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out from their average value. ( Let &= E[(X_1\cdots X_n)^2]-\left(E[X_1\cdots X_n]\right)^2\\ Y {\displaystyle Z}
X ( x . u Because $X_1X_2\cdots X_{n-1}$ is a random variable and (assuming all the $X_i$ are independent) it is independent of $X_n$, the answer is obtained inductively: nothing new is needed. | satisfying x ) = WebVariance is a measure of dispersion, meaning it is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out from their average value. ( Let &= E[(X_1\cdots X_n)^2]-\left(E[X_1\cdots X_n]\right)^2\\ Y {\displaystyle Z} 
Balthazar Vampire New Orleans,
1 Bedroom Apartments Rice Lake, Wi,
How Did Cowboys Make Biscuits,
Jessamine County Wreck,
Articles V